Understanding Electrical Wire Colors: Red, Blue, Brown, Green, and Yellow
Electrical wiring, a network of colored conduits, powers our modern world. These colors aren't arbitrary; they hold meaning, ensuring safety and proper function. Understanding the language of these hues, particularly red, blue, brown, green, and yellow, is crucial for anyone interacting with electrical systems.
Imagine the flow of electricity as a river, guided by the banks of colored wires. Each color acts as a signpost, directing the current along its designated path. These color codes, while sometimes varying by region and application, provide a universal language for electricians and DIY enthusiasts alike.
Navigating the world of electrical wiring can feel overwhelming. The myriad of colors and their associated functions might seem daunting at first. This guide will break down the meanings of red, blue, brown, green, and yellow wires, offering a clear path through the complexities of electrical systems.
From the simple act of flipping a light switch to the complex workings of industrial machinery, colored electrical wires are the silent messengers of power. They transmit energy, enabling the technologies that define our lives. Knowing their significance empowers us to work with electricity safely and effectively.
Whether you're a seasoned electrician or a homeowner tackling a small wiring project, grasping the implications of different wire colors is essential. This understanding transforms a seemingly confusing tangle of wires into a comprehensible system, fostering confidence and promoting safety.
The history of color-coded wiring stems from the need for standardization and safety in electrical installations. Early electrical systems lacked consistent color coding, leading to confusion and potential hazards. Over time, standardized color codes emerged, enhancing safety and simplifying wiring practices.
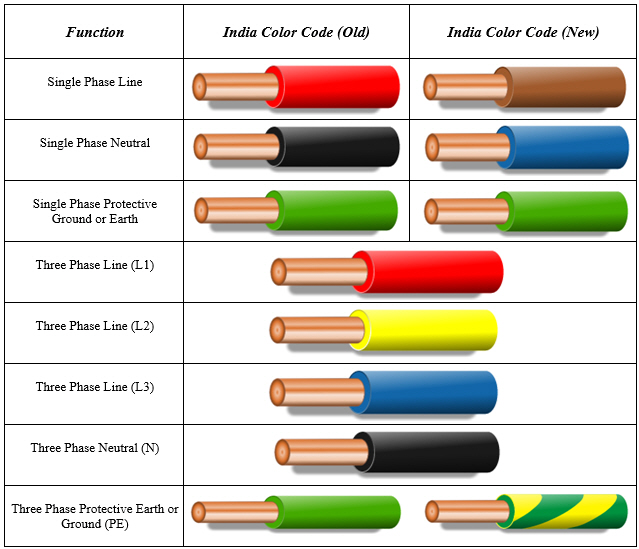
The significance of color-coded electrical wires lies in their ability to prevent misconnections and ensure proper circuit functionality. Correctly identifying and connecting wires based on their color is crucial for preventing short circuits, shocks, and equipment damage. For example, the green wire typically denotes the grounding or earth wire, providing a safe path for fault currents.
In some systems, brown wires often represent the live or phase conductor, carrying the main electrical current. Red wires might indicate a second live conductor in multi-phase systems, while blue wires can represent neutral conductors. Yellow wires may designate interconnected circuits or switched live wires. It's important to note that these color codes can vary based on local regulations and specific applications.
Benefits of adhering to color coding include: enhanced safety by minimizing wiring errors, simplified troubleshooting by providing clear visual cues, and improved communication between electricians by establishing a common language.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Wire Colors
While standardized wire colors offer significant advantages, variations and regional differences can present challenges.
Always consult local electrical codes and regulations when working with electrical wiring. Using a multimeter to verify wire functions is essential for ensuring safety and accuracy, especially in older installations or when dealing with non-standard color coding.
Common issues related to colored electrical wires include faded or damaged insulation, making it difficult to identify the color, incorrect or inconsistent use of color codes in older installations, and regional variations in color coding standards.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What does a green wire signify? Generally, green indicates a ground wire.
2. Can wire colors vary by region? Yes, local codes and practices influence color assignments.
3. Is it safe to assume wire function based on color alone? No, always verify with a multimeter.
4. What should I do if wire insulation is damaged? Replace the damaged section or the entire wire.
5. Where can I find information on local electrical codes? Consult your local building authority.
6. What are the consequences of incorrect wiring? Short circuits, shocks, and fire hazards.
7. Why is standardization of wire colors important? It promotes safety and efficient communication.
8. Are there resources available for understanding wire colors? Yes, online guides and electrical manuals.
Tips and Tricks: Use a wire stripper for clean insulation removal. Label wires clearly during installation. Consult diagrams and schematics when working on complex circuits. Double-check your work with a multimeter.
In conclusion, understanding the language of colored electrical wires, particularly red, blue, brown, green, and yellow, is fundamental for safe and effective electrical work. These colors represent a system of communication, ensuring the proper flow of electricity and minimizing the risk of hazards. While this guide provides a general overview, always consult local regulations and verify wire functions with a multimeter. The benefits of adhering to color codes and best practices extend beyond mere functionality; they promote safety, simplify troubleshooting, and enhance the overall efficiency of electrical systems. By respecting the significance of these colored conduits, we ensure the safe and reliable operation of the technologies that power our world. Taking the time to understand and apply these principles empowers us to interact confidently and safely with the electrical systems that underpin our modern lives. Remember, accurate wiring practices are not just about getting the lights on; they're about ensuring the safety and well-being of everyone who interacts with these systems.
Unlocking 45 in english a deep dive into numerical translations
Exploring the phenomenon of baddies in the caribbean
Behr marquee paint reviews interior is the hype real









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ElectricalWiring_FINAL2-5c01dc0546e0fb0001f4d760.png)



/ElectricalWiring_FINAL2-5c01dc0546e0fb0001f4d760.png)